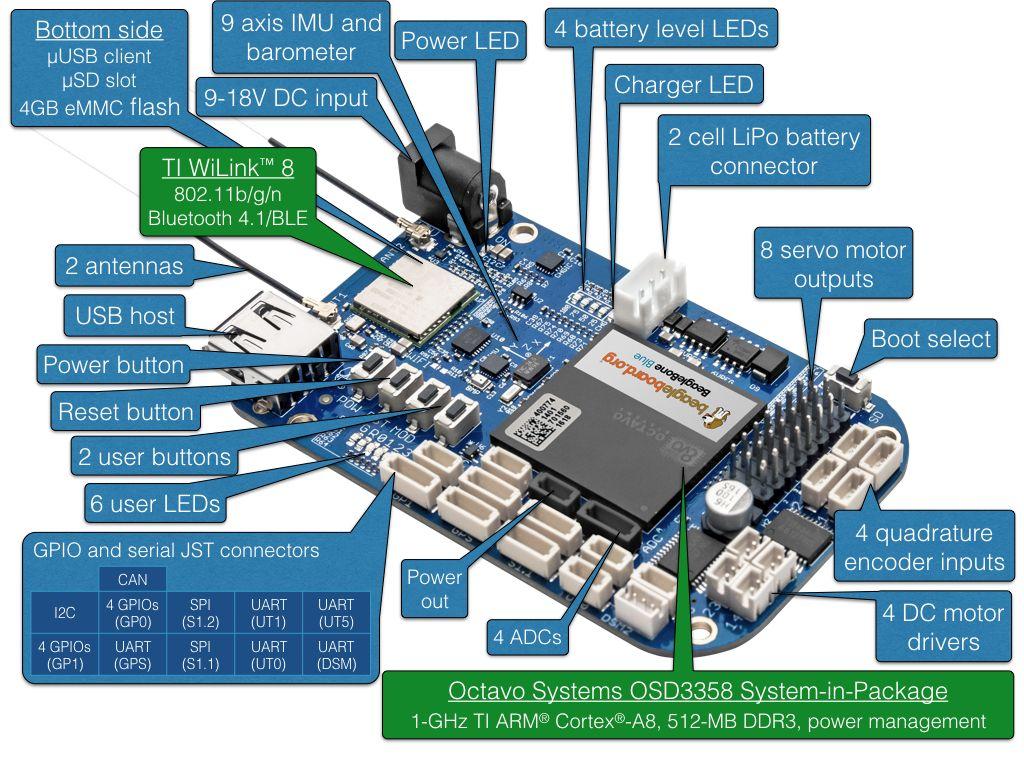
BeagleBone Blue
PX4 support for this flight controller is experimental.
BeagleBone Blue 是一台基于 Linux 的一体机。 它针对机器人技术进行了优化,这种紧凑且便宜的电路板具有飞行控制器所需的所有必要传感器和外围设备。 本主题说明如何设置电路板以使用 librobotcontrol 机器人软件包运行 PX4。
操作系统映像
可以在这里找到 BeagleBone Blue 图像:
- 最新的稳定 OS 映像。
- 测试 OS 映像(经常更新)。
有关闪存操作系统映像的信息可以在 this page 上找到。 其他有用的信息可以在 FAQ 中找到。
Optionally you can update to a realtime kernel, and if you do, re-check if librobotcontrol works properly with the realtime kernel.
The latest OS images at time of updating this document is bone-debian-9.9-iot-armhf-2019-08-03-4gb.img.xz.
Cross Compiler Build (Recommend)
The recommended way to build PX4 for BeagleBone Blue is to compile on a development computer and upload the PX4 executable binary directly to the BeagleBone Blue.
This approach is recommended over native build due to speed of deployment and ease of use.
The PX4 build requires librobotcontrol which is automatically included in the build (but it can be installed and tested independently if required).
Beaglebone Blue WIFI Setup
For easy access to your board, you can connect it to your home network via wifi.
The steps are (execute on the board):
sudo su
connmanctl
connmanctl>scan wifi
connmanctl>services
#(at this point you should see your network SSID appear.)
connmanctl>agent on
connmanctl>connect <SSID>
connmanctl>quit
SSH root Login on Beaglebone
Root login can be enabled on the board with:
sudo su
echo "PermitRootLogin yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config && systemctl restart sshd
Cross Compiler Setup
First set up rsync (this is is used to transfer files from the development computer to the target board over a network - WiFi or Ethernet). For rsync over SSH with key authentication, follow the steps here (on the development machine):
Generate an SSH key if you have not previously done so:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
1. ENTER //no passphrase
2. ENTER
3. ENTER
2. Define the BeagleBone Blue board as `beaglebone` in **/etc/hosts** and copy the public SSH key to the board for password-less SSH access:
ssh-copy-id root@beaglebone
3. Alternatively you can use the beaglebone's IP directly: ```ssh-copy-id root@<IP>```
4. When prompted if you trust: yes
5. Enter root password
Cross Compile Setup
Toolchain download
First install the toolchain into /opt/bbblue_toolchain/gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf. Here is an example of using soft link to select which version of the toolchain you want to use:
mkdir -p /opt/bbblue_toolchain/gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf chmod -R 777 /opt/bbblue_toolchain
ARM Cross Compiler for *BeagleBone Blue* can be found at [Linaro Toolchain Binaries site](http://www.linaro.org/downloads/).
> **Tip** GCC in the toolchain should be compatible with kernel in *BeagleBone Blue*. General rule of thumb is to choose a toolchain where version of GCC is not higher than version of GCC which comes with the OS image on *BeagleBone Blue*.
Download and unpack [gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf](https://releases.linaro.org/components/toolchain/binaries/latest-7/arm-linux-gnueabihf/gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf.tar.xz) to the bbblue_toolchain folder.
Different ARM Cross Compiler versions for *BeagleBone Blue* can be found at [Linaro Toolchain Binaries site](http://www.linaro.org/downloads/).
> **Tip** The GCC version of the toolchain should be compatible with kernel in *BeagleBone Blue*.
General rule of thumb is to choose a toolchain where the version of GCC is not higher than the version of GCC which comes with the OS image on *BeagleBone Blue*.
2. Add it to the PATH in ~/.profile as shown below
```sh
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/bbblue_toolchain/gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf/bin
```
> **Note** Logout and Login to apply the change, or execute the same line on your current shell.
Follow the [Development Environment Setup](https://dev.px4.io/master/en/setup/dev_env_linux_ubuntu.html) instructions.
You may have to edit the upload target to match with your setup:
nano Firmware/boards/beaglebone/blue/cmake/upload.cmake
#in row 37 change [email protected] --> root@beaglebone (or root@<IP>)
Cross Compile and Upload
Compile and Upload
make beaglebone_blue_default upload
Without upload, files stored local in build folder.
To test the uploaded files, run the following commands on the BeagleBone Blue board:
cd /home/debian/px4
sudo ./bin/px4 -s px4.config
Currently librobotcontrol requires root access.
Native Builds (optional)
You can also natively build PX4 builds directly on the BeagleBone Blue.
After acquiring the pre-built library,
- Select the librobotcontrol installation directory, and set it in the
LIBROBOTCONTROL_INSTALL_DIRenvironment variable so that other unwanted headers will not be included - Install robotcontrol.h and rc/* into
$LIBROBOTCONTROL_INSTALL_DIR/include - Install pre-built native (ARM) version of librobotcontrol.* into
$LIBROBOTCONTROL_INSTALL_DIR/lib
Run the following commands on the BeagleBone Blue (i.e. via SSH):
Install dependencies:
sh sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install cmake python-empyClone the PX4 Firmware directly onto the BeagleBone Blue.
- Continue with the standard build system installation.
Chnages in config
All changes can be made in de px4.config file directly on beaglebone. For example, you can change the WIFI to wlan.
If you want to change permanently, you have to change Firmware/posix-configs/bbblue/px4.config on the Build Machine before build.
引导期间自动启动
Here is an example [/etc/rc.local]:
#!/bin/sh -e
#
# rc.local
#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
# bits.
#
# By default this script does nothing.
# wait for services to start up
/bin/sleep 25
cd /home/debian/px4
/home/debian/px4/bin/px4 -d -s /home/debian/px4/px4.config > /home/debian/px4/PX4.log &
exit 0
Below is a systemd service example [/lib/systemd/system/px4-quad-copter.service]:
[Unit]
Description=PX4 Quadcopter Service
After=networking.service network-online.target
StartLimitIntervalSec=0
Conflicts=px4-fixed-wing.service
[Service]
WorkingDirectory=/home/debian/px4
User=root
ExecStart=/home/debian/px4/bin/px4 -d -s /home/debian/px4/px4.config
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=1
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Miscellaneous
动力伺服导轨
When PX4 starts, it automatically applies power to servos.
特殊功能
BeagleBone Blue has some unique features such as multiple choices of WiFi interfaces and power sources. Refer to comments in /home/debian/px4/px4.config for usage of these features.
SBUS 信号转换器
SBUS signal from receiver (e.g., FrSky X8R) is an inverted signal. UARTs on BeagleBone Blue can only work with non-inverted 3.3V level signal. This tutorial contains a SBUS signal inverter circuit.
典型连接
For a quadcopter with GPS and an SBUS receiver, here are typical connections:
Connect the ESC of motor 1, 2, 3 and 4 to channel 1, 2, 3 and 4 of servo outputs on BeagleBone Blue, respectively. If your ESC connector contains a power output pin, remove it and do not connect it to the power output pin of the servo channel on the BeagleBone Blue.
Connect the above mentioned converted SBUS signal to the dsm2 port if you have the matching connector for dsm2, otherwise connect it to any other available UART port and change the corresponding port in /home/debian/px4/px4.config accordingly.
Connect the signals of GPS module to GPS port on the BeagleBone Blue. Note that the signal pins of the GPS port on the BeagleBone Blue are only 3.3V tolerant, so choose your GPS module accordingly.

